Air source heat pumps are becoming a popular choice for heating and cooling homes and buildings. They are efficient, eco-friendly, and can save you money on energy bills. But how do they work, and what makes their technology so special? In this article, we’ll explain the working principles of air source heat pumps and dive into the key technologies that make them effective. We’ll break it down into clear sections to help you understand everything you need to know.
What Is an Air Source Heat Pump?
An air source heat pump is a device that uses heat from the outside air to warm or cool a building. It can provide heating in winter, cooling in summer, and even hot water for your home. Unlike traditional systems that burn fuel to create heat, air source heat pumps move heat from one place to another using electricity. This makes them much more efficient and better for the environment.
There are two main types of air source heat pumps: air-to-air and air-to-water. Air-to-air pumps heat or cool the air inside a building, while air-to-water pumps transfer heat to a water-based system, like radiators or underfloor heating.
How Does an Air Source Heat Pump Work?
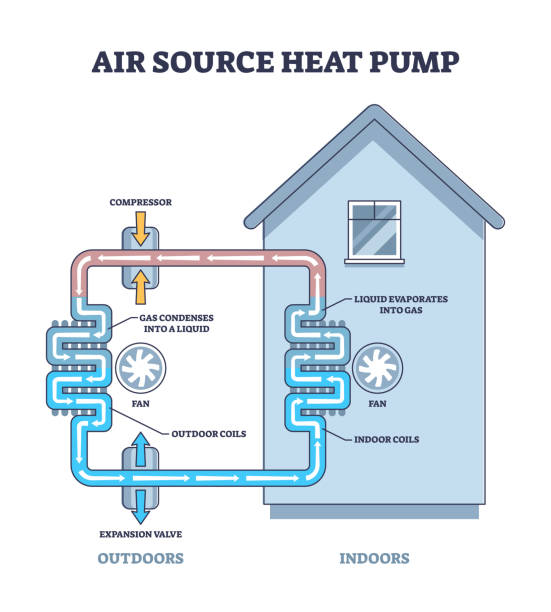
The working principle of an air source heat pump is based on a simple process that captures heat from the air and transfers it to your home. Even when it’s cold outside, the air contains some heat energy that the pump can use. Here’s how it works, step by step:
- Heat Absorption: A fan pulls outside air into the heat pump. The air passes over an evaporator coil filled with a special liquid called a refrigerant. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the air, even at low temperatures like 0°F, and turns into a gas.
- Compression: The gaseous refrigerant flows into a compressor. The compressor squeezes the gas, which increases its temperature significantly, often to 140°F or higher. This hot gas is now ready to transfer heat.
- Heat Transfer: The hot gas moves to a condenser, where it releases its heat. In an air-to-air system, the heat warms the air that’s blown into your home. In an air-to-water system, like the NEWNTIDE air to water Heat Pump, the heat is transferred to water for radiators, underfloor heating, or hot water tanks.
- Expansion: After releasing its heat, the refrigerant cools down and turns back into a liquid. It passes through an expansion valve, which lowers its pressure and temperature. The cold liquid is now ready to absorb heat from the outside air again, and the cycle repeats.
This process uses electricity to run the fan, compressor, and other components, but most of the heat comes from the air, not the power supply. This is why air source heat pumps are so efficient.
Key Technologies in Air Source Heat Pumps
The efficiency and performance of air source heat pumps rely on several advanced technologies. These features make them reliable, versatile, and cost-effective. Let’s look at the most important ones.
Refrigerant Technology
The refrigerant is the heart of the heat pump’s operation. It’s a special fluid that can absorb and release heat at low temperatures. Modern air source heat pumps use eco-friendly refrigerants, like R32 or R410A, which have a lower environmental impact than older types. These refrigerants are designed to work efficiently in a wide range of temperatures, ensuring the pump performs well in both warm and cold climates.
Compressor Efficiency
The compressor is a critical component that determines how well the heat pump works. Most modern pumps use inverter compressors, which can adjust their speed based on the heating or cooling demand. This makes the system more efficient than older fixed-speed compressors, as it avoids wasting energy when less heat is needed. Inverter technology also reduces wear and tear, extending the pump’s lifespan.
Heat Exchanger Design
Heat exchangers, like the evaporator and condenser, are where the heat transfer happens. Advanced designs use materials like copper or aluminum for better heat transfer and durability.
Smart Controls
Many air source heat pumps come with smart control systems. These allow you to adjust the temperature, schedule operation, or monitor energy use from your phone or a touchscreen panel. Smart controls can optimize the pump’s performance by adjusting settings based on weather conditions or your daily routine, saving energy and improving comfort.
Low-Temperature Performance
Older heat pumps struggled in very cold weather, but new models are designed to work efficiently at temperatures as low as -15°F or even -20°F. This is thanks to improved refrigerants, enhanced compressors, and defrost systems that prevent ice buildup on the outdoor unit. These advancements make air source heat pumps a viable option in colder regions.
Benefits of Air Source Heat Pump Technology
The technology behind air source heat pumps offers several advantages that make them stand out compared to traditional heating systems.
High Energy Efficiency
Air source heat pumps are incredibly efficient. They can produce three to four times more heat energy than the electricity they use. This efficiency is measured by the Coefficient of Performance (COP), which typically ranges from 3 to 4. For example, a COP of 3 means you get three units of heat for every unit of electricity. This can cut your energy bills significantly compared to electric or gas heaters.
Eco-Friendly Operation
Because they use heat from the air instead of burning fuel, air source heat pumps produce far fewer carbon emissions. If your electricity comes from renewable sources, like solar or wind, the system can be nearly carbon-neutral. This makes them a great choice for reducing your environmental impact.
Versatility
Air source heat pumps can heat, cool, and provide hot water, making them a year-round solution. Whether you need to warm your home in winter or cool it in summer, a single system can handle it all. This versatility reduces the need for separate heating and cooling equipment.
Quiet Operation
Modern air source heat pumps are designed to run quietly. Improved fan designs and sound-dampening materials keep noise levels low, often below 50 decibels, similar to a quiet conversation. This makes them suitable for residential areas where noise could be a concern.
Challenges and Solutions
While air source heat pumps are highly effective, they do face some challenges. One issue is their performance in very cold weather, where efficiency can drop. However, modern models with low-temperature technology and hybrid systems that switch to backup heating solve this problem. Another challenge is the upfront cost, which is higher than traditional systems. But energy savings and government incentives often offset this over time.
Installation can also be tricky, as the outdoor unit needs space and proper airflow. Working with a reputable manufacturer like Guangdong New Energy Technology Development Co., Ltd ensures you get a model suited to your space and climate.
What to Consider Before Buying
If you’re thinking about getting an air source heat pump, here are a few things to keep in mind:
- Climate: Make sure the model is designed for your local weather, especially if you live in a cold area.
- Size: Choose a unit that matches your home’s heating and cooling needs. A professional can help calculate the right size.
- Installation: Hire a qualified technician to ensure proper setup and performance.
- Incentives: Check for government rebates or tax credits that can lower the cost.
Conclusion
Air source heat pumps are an efficient and eco-friendly way to heat and cool your home. Their working principle—moving heat from the air using a refrigerant cycle—is simple yet powerful. Advanced technologies like inverter compressors, eco-friendly refrigerants, and smart controls make them reliable and cost-effective. If you’re looking to save energy and reduce your environmental impact, an air source heat pump is a smart choice.